It is estimated that 7,400 Canadians will be diagnosed with head and neck cancer in 2021, and 2,100 Canadians will die as a result. Oral cancer can affect the mouth, lips, tongue, or throat and is identified through regular oral cancer screening. This is not something your regular health care practitioner includes in your physical examinations.
Instead, oral cancer screenings are provided by your dentist. Here we explain everything you need to know about oral cancer and why it is so important to have your regular oral cancer screening at your dental checkups.
What Is Oral Cancer?

Oral cancer forms in the cells of the mouth when the cells change in their growth or behaviour. This can form a cancerous tumour which can destroy healthy tissue and continue to grow. The longer oral cancer remains untreated, the higher risk there is for it to spread to areas such as the lymph nodes and neck.
While tumours in the area can be non-cancerous, early detection is very important so cancer can be ruled out. As well, if changes to the cells are noticed early, it could be a precancerous condition that can be treated before cancer develops. Luckily your dentist performs a complete oral cancer screening at your dental checkups. So while you might feel your dental checkups aren’t that important, it is the best way to detect oral cancer or precancerous conditions of the mouth and neck.
Where Can Oral Cancer Occur?
There are several areas where oral cancer can occur, including:
- Lips
- Soft palate
- Tonsils
- Tongue
- Uvula
- Floor of the mouth
- Inner lining of the cheeks
- Upper or lower jawbone
- Hard palate
- Gums
- Alveolar ridge where the teeth sockets are located
- Teeth
This is why oral cancer screenings are performed by your dentist. They are oral healthcare experts who can identify issues and recommend the required testing for a proper diagnosis.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Oral Cancer?
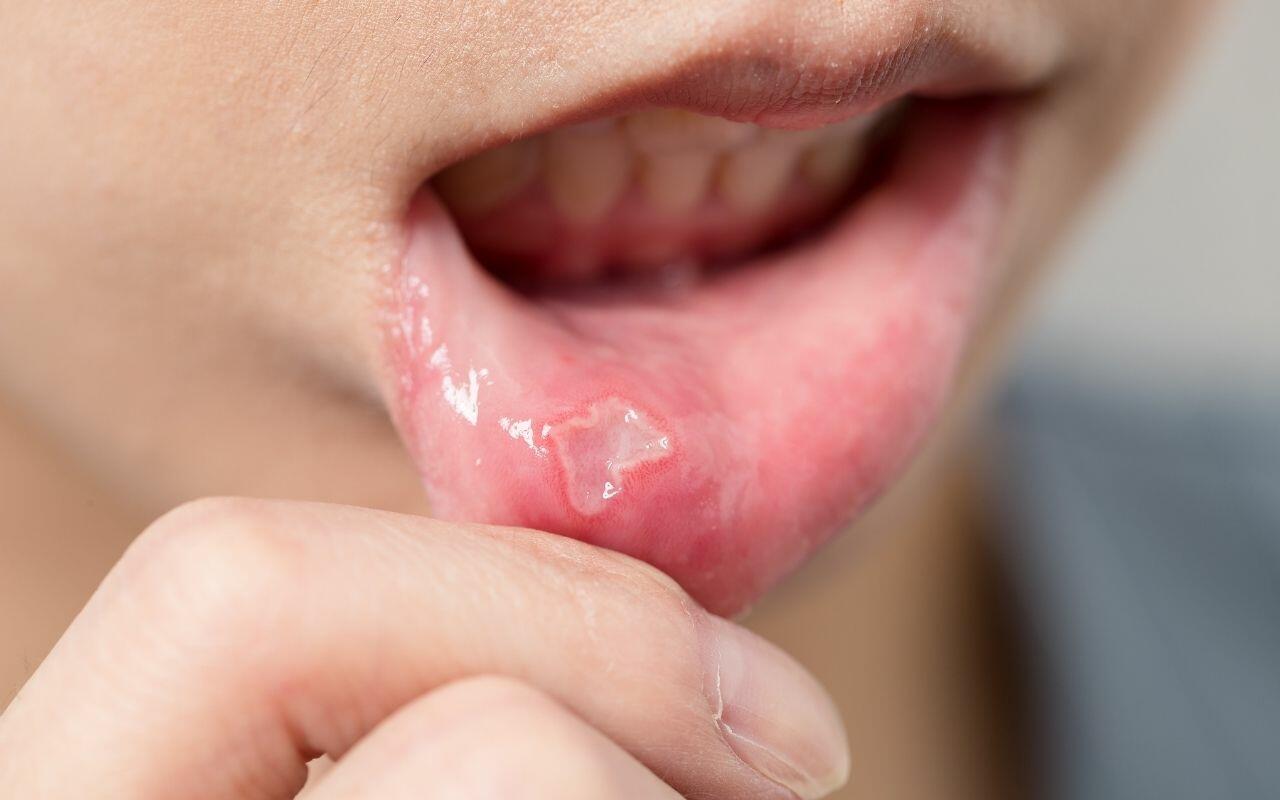
The most common signs and symptoms of oral cancer include:
- Discolouration on the mouth, lips, or tongue
- Lumps in the mouth or along the jaw bone
- Changes in the texture or colour of the mouth tissue
- Bleeding or numbness in the mouth
- Ongoing sores in the mouth that don’t heal
- Patches in the mouth that don’t heal
- Difficulty swallowing
- Changes to taste
- Odd sensations in the tongue
If you notice any of these symptoms, set up an appointment with your dentist right away.
What Are The Risk Factors For Oral Cancer?
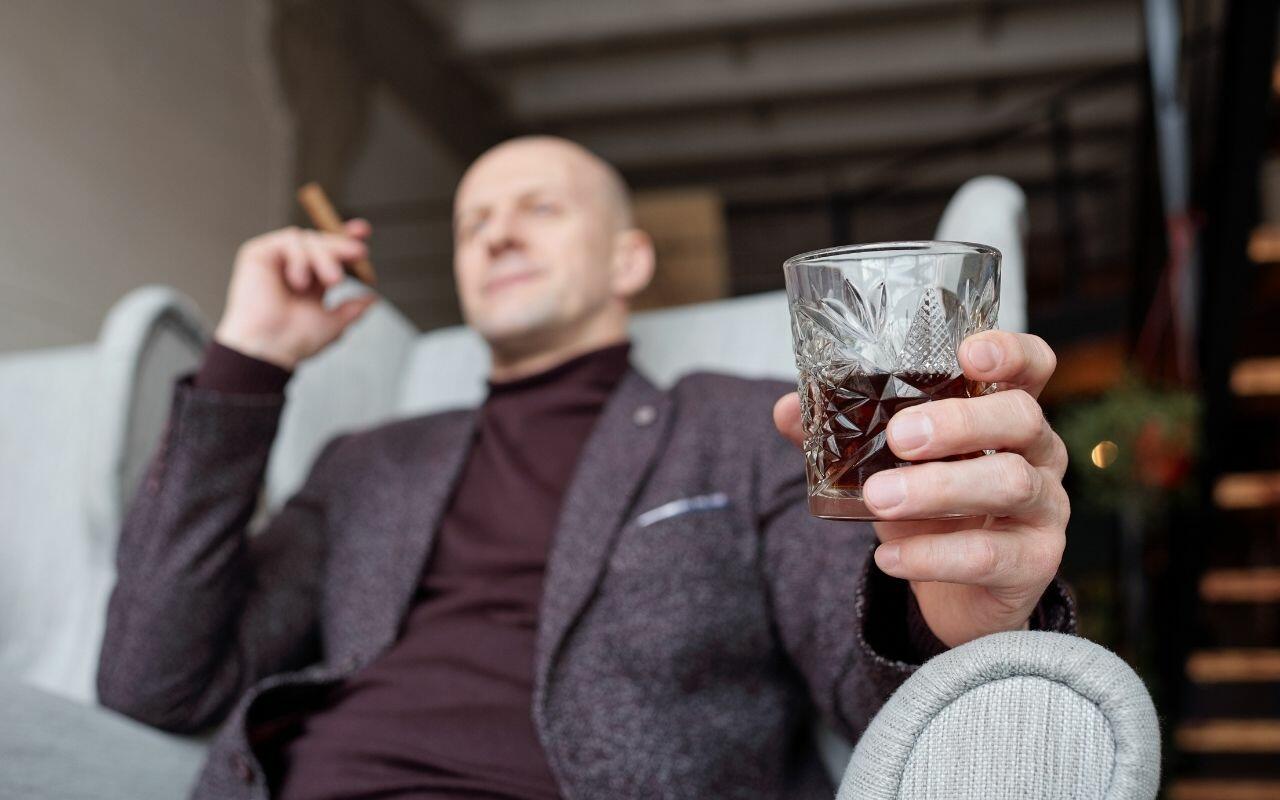

There are several factors that can increase your risk for oral cancer including:
- Smoking or chewing tobacco products
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Oral sex
- Exposure to the sun over prolonged periods of time
- Poor diet
- Being male
- Genetics
- A history of leukoplakia
Recent studies have also shown a possible tie between the HPV virus, a sexually transmitted condition, and oral cancer.
How Is Oral Cancer Diagnosed?
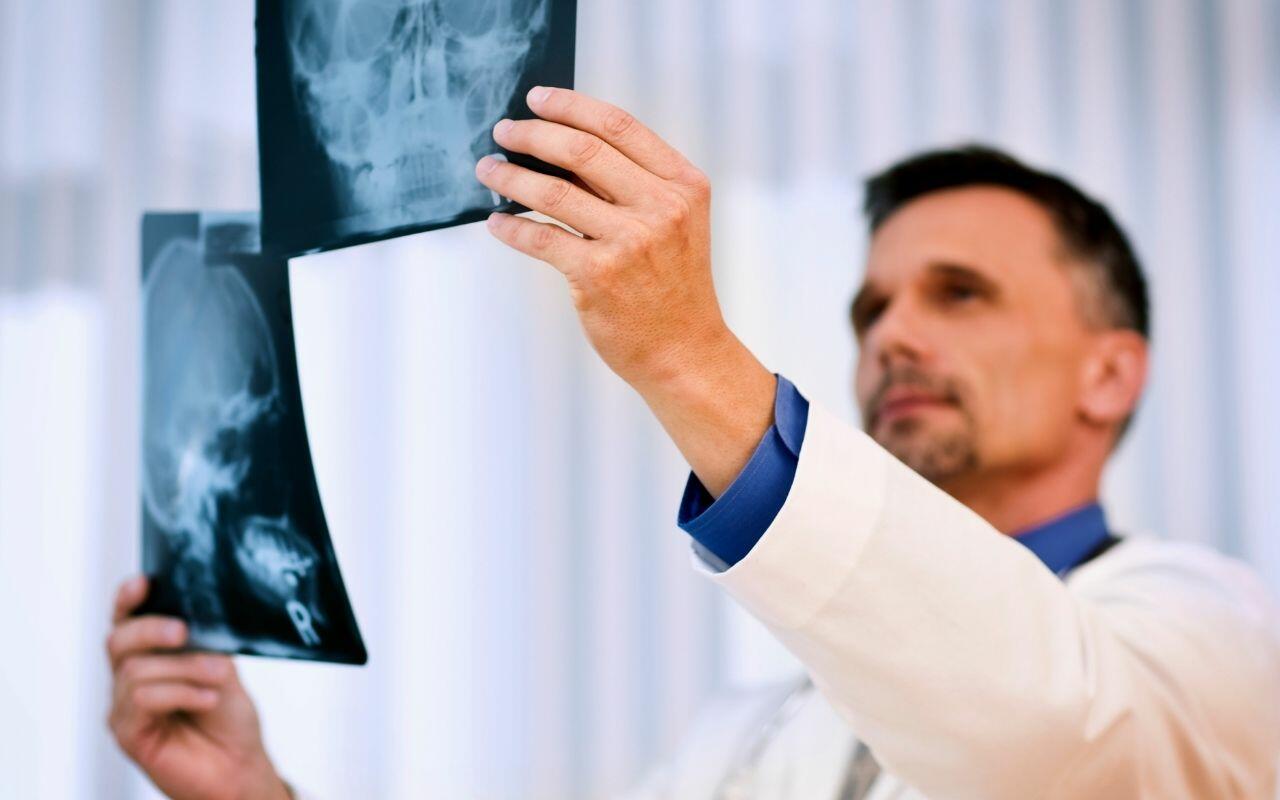
Oral cancer diagnosis starts with an oral cancer screening which includes:
- An examination of your mouth to check for red or white patches or mouth sores
- Feeling the tissues in your mouth to check for lumps or other abnormalities
- Throat and neck exams to check for lumps
If your dentist finds any abnormalities, they might do additional tests such as:
- Oral cancer screening dye to spot more abnormal cells in your mouth
- Oral cancer screening light to look for abnormalities
- Follow up to see if abnormal patches are still present or have changed
- A biopsy of lumps
- X-rays, ultrasounds, CT scans, or MRIs
These further tests will help your dentist determine if you have cancer, or what further steps might be needed.
What Is A Biopsy?
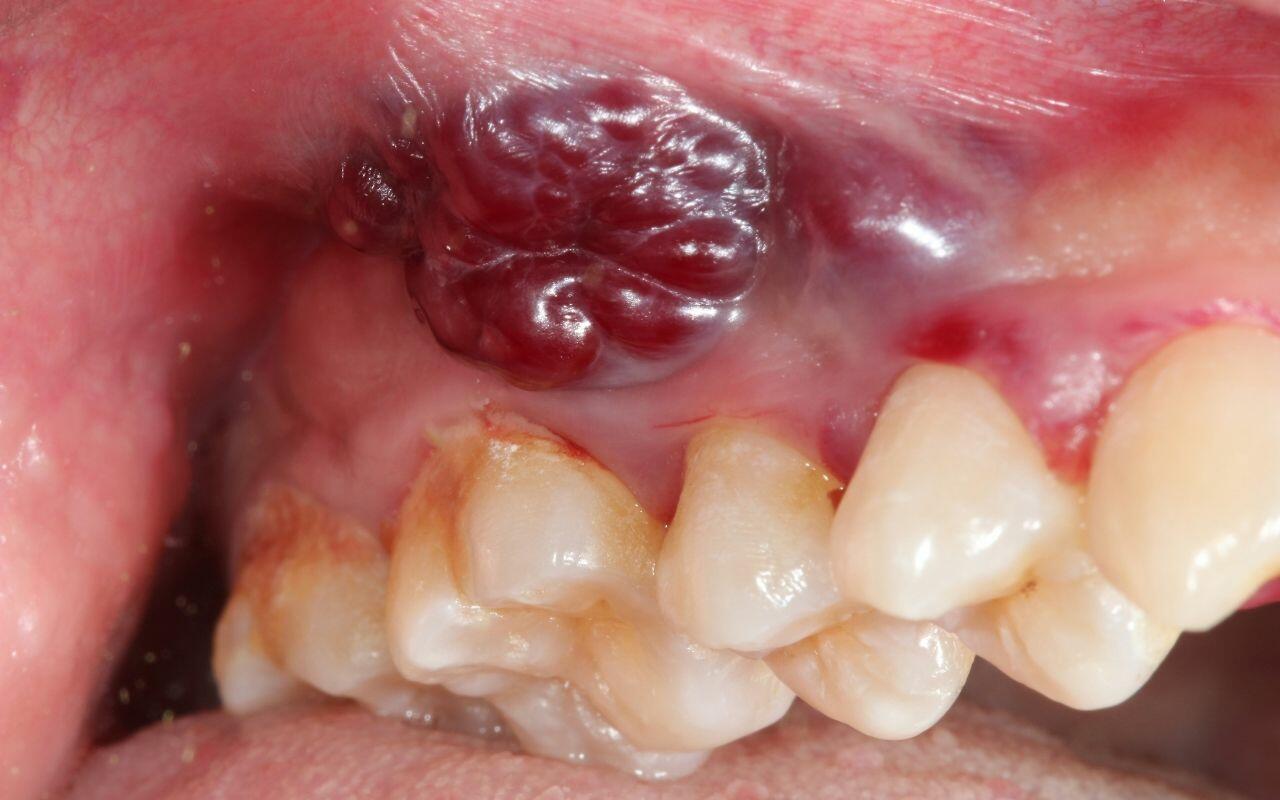
Biopsies examine the cellular level of a lesion to determine if it is benign (noncancerous), cancerous, or has the potential to form a malignancy (cancer). Dentists can perform what is called brush cytology, but a biopsy is still required to confirm a cancer diagnosis.
Treatment Of Oral Cancer

Treatment is determined based on the particular case but can include:
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Removal of tumours through surgery
Sometimes a combination of treatments might be required to help improve outcomes.
Can Oral Cancer Be Prevented?
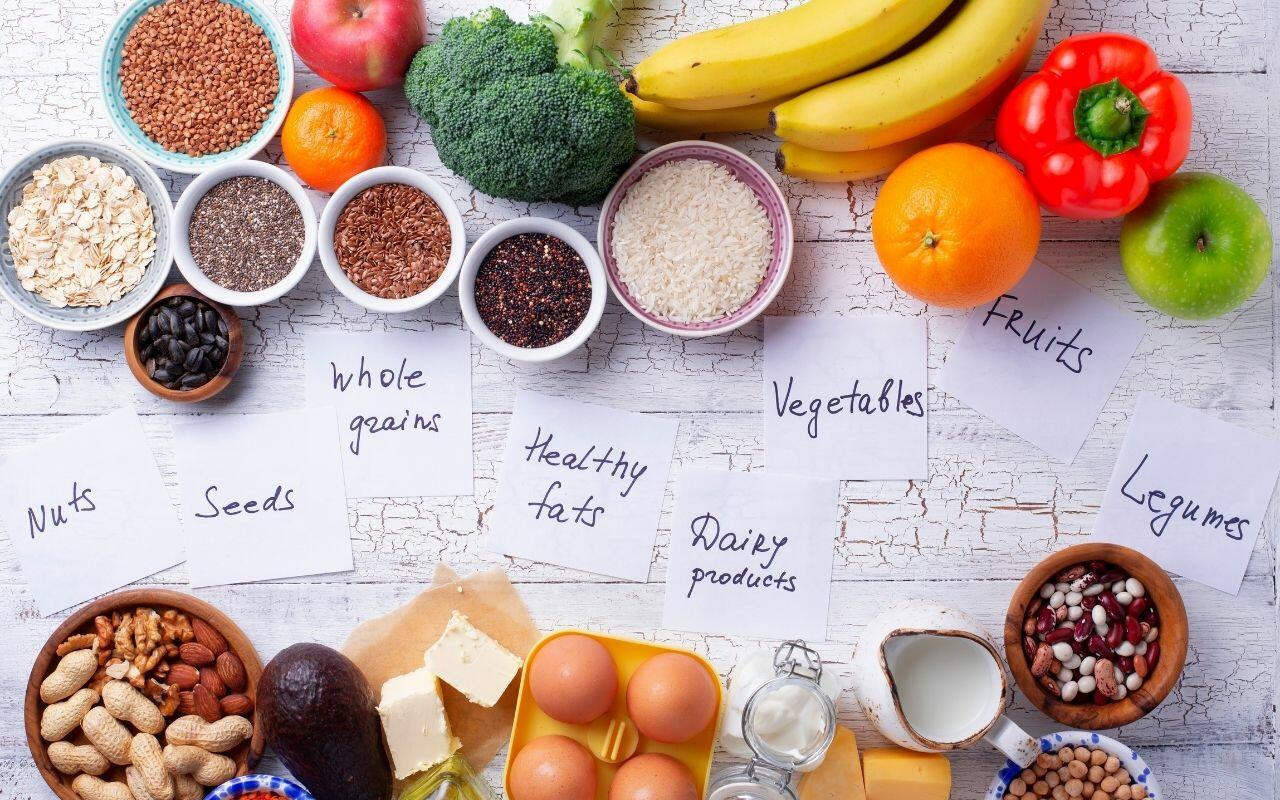

While it is not possible to guarantee you can prevent any form of cancer or disease, you can certainly take steps to reduce your risk including:
- Scheduling your regular dental exams for your oral cancer screenings
- Quitting the use of tobacco
- Limiting your alcohol consumption
- Using UV protection and limiting your exposure to the sun
- Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Watching for signs and symptoms of oral cancer and calling your dentist right away
- Females can also have the HPV vaccine if not yet diagnosed with the virus
Oral cancer screening is your best defense for early detection and diagnosis of oral cancer or precancerous conditions of the mouth.
Self-Examination For Oral Cancer

Don’t be afraid to ask your dentist for a “guided tour” of the areas you can check at home. If you feel you are at higher risk for oral cancers, your dentist can explain what areas to check regularly, as well as what types of tissue changes can be spotted with the human eye. This allows you to identify potential issues even sooner, so you can arrange a full dental oral cancer screening if you find anything you feel is suspect. This would include feeling your neck and jaw for lumps, checking your inner cheeks, gums, and tongue for discolourations, and also reporting changes to your sense of taste.
Your dentist helps create awareness about oral cancer and actively screens patients for suspect tissue and lumps at routine screenings. They are a major member of your overall healthcare team, providing valuable preventative care for not just your teeth and gums, but for oral cancer as well. They are your best defense against the progression of oral cancers. Dentists provide a critical early diagnosis to ensure treatment is provided in the early stages and improve your odds for positive outcomes.
Call today to schedule an appointment at 905-775-5307 or click here to request an appointment.
